Hello everyone!
.
I wanted to post a lesson up that uses one of my approaches to harmonizing scales from my Harmonic Combinatorics book. It’s a cool way to not only get away from stock voicings but also to generate new lines as well!
I’m using C Major as the tonal center for this lesson but the approach can (and probably should be) be adapted to any scale.
.
A couple of lessons ago, I talked about the modal microscope – which was a term I used to discuss examining modes on multiple levels and the advantage of viewing modes as subsets of a parent scale. Before I get into the harmonization approach I want to expand on this idea of the microscope analogy and apply it to harmony.
.
The Harmonic Microscope
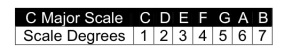
If I harmonize a parent major scale in the key of C, I’ll end up with the following chords on each scale degree.
.

.
So if you’re playing in the key of C and want to get into more harmonic depth on an E minor chord, it’s time to reach into your chord bag and pull out your stock minor 11 (b9, b13) voicing. Oh, you don’t have one? Don’t worry – most guitarists don’t. Learning stock voicings and inversions for this specific chord form probably isn’t the best use of your time anyway.
Using the microscope analogy, this is really looking at the chord on a 2x setting.
.
Here’s the 1x setting for this example:
playing any combination of the notes from C Major over the root E creates some variant of an
E min / min7 / min7 (b9) / min 11 (b9, b13) chord.
.
And here’s the bigger picture:
Once you are aware of the types of sounds that are created from various chord types, you can start thinking about chords and chord voicings on the macro (i.e. parent scale) level. This means that if I’m playing over a D minor chord and using notes from the C major scale, I don’t have to analyze each indidual chord because I know it’s all under some type of generic D minor 7/minor 9/minor 11 or minor 13 umbrella.
.
Harmonic Combinatorics
Harmonic Combinatorics refers to a process of identifying “countable discrete structures” harmonically. In other words, it examines unique combinations of notes on all of the possible string combinations for the purposes of develop harmonic and melodic possibilities. One way to do this is through a method that I use to generate unique ideas through a process that some people refer to as spread voicings.
.
A Systematic Method For Harmonizing Any Scale Or Mode On The Guitar
It’s important to state at the outset that the method I’m employing is only one possible way to approach this exploration. I’ve taken this approach to maximize the number of unique voicings, but you should feel free to take any of the rules that I’ve applied to this approach (like eliminating octaves) with a grain of salt. The object is to gain new sounds – so change the patterns here in whatever ways necessary.
.
Here’s an approach that will give you more voicings and lines than you might have thought possible.
.
- Step 1: Write out a scale and write the scale degree under each note.
(Example: C Major)
.
- Step 2: On a blank chord sheet – write out the scale degrees on each string up to the 5th fret.
.
(To clarify: The numbers on the left hand side of the diagram are the fret numbers ).
.

.
- Step 3: Starting with the lowest note on the lowest string, write out all the initial voicing of all possible 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 note harmonies by scale degree on different string sets.
.
For example, if I was looking at the G, B and high E strings, some sample initial voicings would be
573, 574, 576, 513, 514, 516, 523, 524, 526, 534, 536
673, 674, 675, 613, 623
713, 723
173, 174, 175, 176, 123
.
You may have noticed that I skipped some voicings:
.
If you want to save some time and increase the number of unique chords try the following parameters:
.
- No doubling of chord tones (Ex. 363). (Again – if you like that sound – use it! but the point of this process is to generate unique voicings with unique notes.)
- At least one note in the voicing has to be the lowest on a string. If you look at 614 on the G, B and high E strings you’ll see that it’s really the second voicing of 573 on the frets below it. Having at least one note be the bottom note on any string will help ensure that you’re not just working out voicings that you may have already done.
- The highest fret to be used in the first voicing is the 5th fret. This last step is going to produce some voicings that aren’t playable on the lower frets, but might work in the upper registers.
.
- Step 4: Select a string set and move the voicing in scale-wise motion up the strings to the octave.
.
For the purposes of this lesson – I’m going to focus primarily on 3 string groups, but this idea is applicable on any 2-6 string set of strings. (It’s worth mentioning that – Harmonic Combinatorics does all the work for this process for all string sets – (it’s also why it’s over 400 pages long!!)).
.
.
.
(Again, while this book follows this process through the key of C Major, this process can be applied to any tonal center.)
.
- I’ve written out an example based on the D, G and B string set (i.e. 432) and gone with an initial voicing of a F, G and D (or 452).
.
(Note: The reason I start with numbers instead of notes is 1. It’s a lot easier to see if I’ve missed a number in a sequence when working these things out and 2. It eliminates the initial step of wondering what harmony I’m creating. This is simply a process that I’ve used with good results. If the numbering is weird for you, just use what works for you.)
.
.
.
- This creates seven different voicings which could be played as a modal chord progression, used as the basis for a melodic idea or even isolated into individual chords. If this process yields even one chord that you like it’s worthwhile.
.
- The function of the voicings will depend on the root. If you want to dig deeper into this area, you can use other notes as a root (note Harmonic Combinatorics includes a chart which shows all chord tones based on scale degree). I’ve posted the sound of the chords being played against an A root below. A was picked as a root because it’s an open string, but you could just as easily tap any note from the C major scale to create various modal sounds:
.
- Playing C as the bass note will give you C Ionian sounds
- Playing D as the bass note will give you D Dorian sounds
- Playing E as the bass note will give you E Phrygian sounds
- Playing F as the bass note will give you F Lydian sounds
- Playing G as the bass note will give you G Mixolydian sounds
- Playing A as the bass note will give you A Aeolian sounds
- Playing B as the bass note will give you B Locrian sounds
.
Check out these chord sounds over A. In addition to possible comping ideas, these can be arpeggiated for melodic ideas as well.
.
.
A few notes on working with voicings
.
Here are some additional points to consider when using this process:
.
- Common sense is your friend. If a chord seems difficult to play:
.

.
there is almost always an easier way to play it on another string set.
.
.
Since the voicings presented are in the key of C Major with no sharps or flats, the information (and approach) here is easily adaptable to other scales, modes etc…
.
- If you find a voicing in C Major you like, just move it to whatever other key you’re playing in.
- To create all of the C Melodic Minor (i.e. Jazz Minor) voicings – just change any E to Eb.
- To create all of the C Harmonic Minor voicings – just change any E to Eb and any A to Ab.
.
Now I’ll talk about making melodic lines from this material.
.
Melodic Variations
.
As I mentioned earlier, these voicings can be played as melodies simply by playing the notes one at a time. In The GuitArchitect’s Positional Exploration and the GuitArchitect’s Guide to Modes: Melodic Patterns, I’ve outlined a series of methods for generating melodic variations. But since this approach is about combining things, it makes sense to at least look at some melodic possibilities with regards to note choice. I’ve decided to take a three-note voicing as it offers enough possibilites to be interesting, but not too many to be over-whelming and have chosen this pattern simply because I like the first voicing.
.
.
It sounds a little deceptive if you play it as is. This is because the first voicing is actually a G major chord in 1st inversion (i.e. with B in the bass). Here it is with the root of each chord added to the low E string (Try working them out and playing them!! There are come challenging chords there.)
.
.
but when you play it with the B as the lowest note it sounds like a B minor with the b3rd on the B string.
.
.
If you play it without harmonic backing, try changing any F natural to F # and it should sound more pleasing to you.
.
“Variety is the spice of life”
.
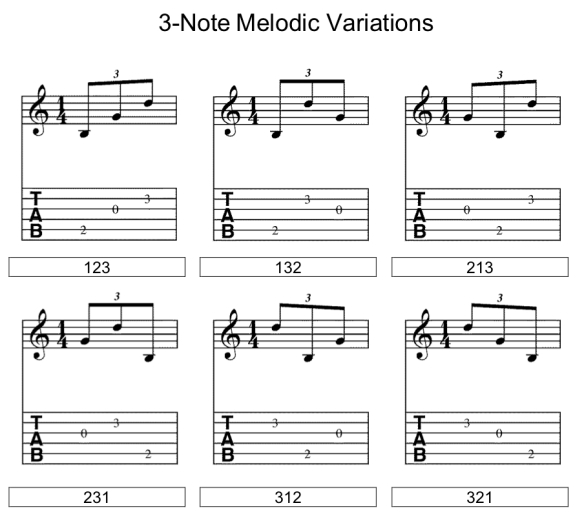
There are six unique melodic variations of any three-note chord or pattern.
.

.
These numbers represent note order. Assigning 1 as the lowest note and 3 as the highest – here are the unique variations on the first three notes.
.
Applying this idea, one possibility for 123 looks like this:
.

.
.
Two things to consider:
.
1. I’ve notated this as triplets for ease of reading, but the very first thing you should probably do (after getting the notes under your fingers is look for a more musical phrasing).
.
.
2. Again, if you play this without harmonic backing this may sound more “right” to you:
.

.
Alternating groups of 123 and 321 for each chord produces:
.

.
.
Combining the first 2 chords into a 6-note pattern allows even more flexibility. Here, I’ve moved the number order around and made a more interesting line.
.

.
.
One part of this phrase has caught my ear:
.

.
When I add a low E root, I get a cool little Phrygian phrase (with a couple of notes snuck in on the high E string).
.
.
The GuitArchitect’s Positional Exploration and the GuitArchitect’s Guide to Modes: Melodic Patterns, has a systematic approach to exploring these types of variations. Having said that, those of you who want to do the work, could just write down a collection of numbers and apply them to different ideas and see what happens.
.
The first important thing, however, is to experiment with different rhythms (including rests!), phrasings (like slides, hammer-on/pull offs) and make some music out this raw material.
.
The second important thing to consider is that with any approach like this you should:
- use them in what you’re currently working on (songs, solos, etc)
- make what you keep part of your sound and discard (or ignore) what you don’t use.
.
I cover some other approaches and break down the theory a little more in depth in Harmonic Combinatorics but I hope this lesson here helps and if you like this idea – you should check out the book (if you haven’t already)!
.
Thanks for reading!
.
-SC
.
If you like this post you may also like:
.
.
Chords/Triads/Superimposition/Arpeggios:
.
.
.
.
.
.